At Osa Property Management, we often field questions about the tax implications of rental property expenses. One common query is whether HOA fees for rental properties are tax deductible.
This blog post will clarify the rules surrounding HOA fees and their potential tax benefits for landlords. We’ll explore the conditions under which these fees may be deductible and offer tips to maximize your rental property tax advantages.
What Are HOA Fees and How Do They Affect Rental Properties?
Definition of HOA Fees
Homeowners Association (HOA) fees represent regular payments property owners make in planned communities or condominiums. These fees fund the maintenance and improvement of shared spaces and amenities. For rental property owners, HOA fees can be deducted as long as you’re renting out the property, impacting profitability and tax considerations.
HOA Fee Structures
HOA fees vary widely based on the community and services provided. A 2023 report by iPropertyManagement indicates that the average monthly HOA fee in the United States ranges from $200 to $300. However, in some luxury communities or major cities, these fees can exceed $1,000 per month. As a rental property owner, you must factor these costs into your overall investment strategy.
Common Expenses Covered by HOA Fees
Typically, HOA fees cover a range of services that benefit the entire community. These often include:
- Landscaping and grounds maintenance
- Exterior building maintenance and repairs
- Trash removal and pest control
- Security services and gated entrances
- Amenities (such as pools, gyms, and clubhouses)
- Insurance for common areas
- Reserve funds for major repairs or improvements
Understanding what your HOA fees cover is essential for an accurate assessment of the value they provide to your rental property and its tenants.
Impact on Rental Property Owners
HOA fees can significantly affect your rental property’s bottom line. Here are some key considerations:
- Rental Pricing: You need to factor HOA fees into your rent calculations to maintain profitability. A 2022 study by Zillow found that properties with HOA fees typically command 4-5% higher rents than similar properties without them.
- Tenant Attraction: Well-maintained shared spaces can enhance the appeal of the community, making it more attractive to potential renters.
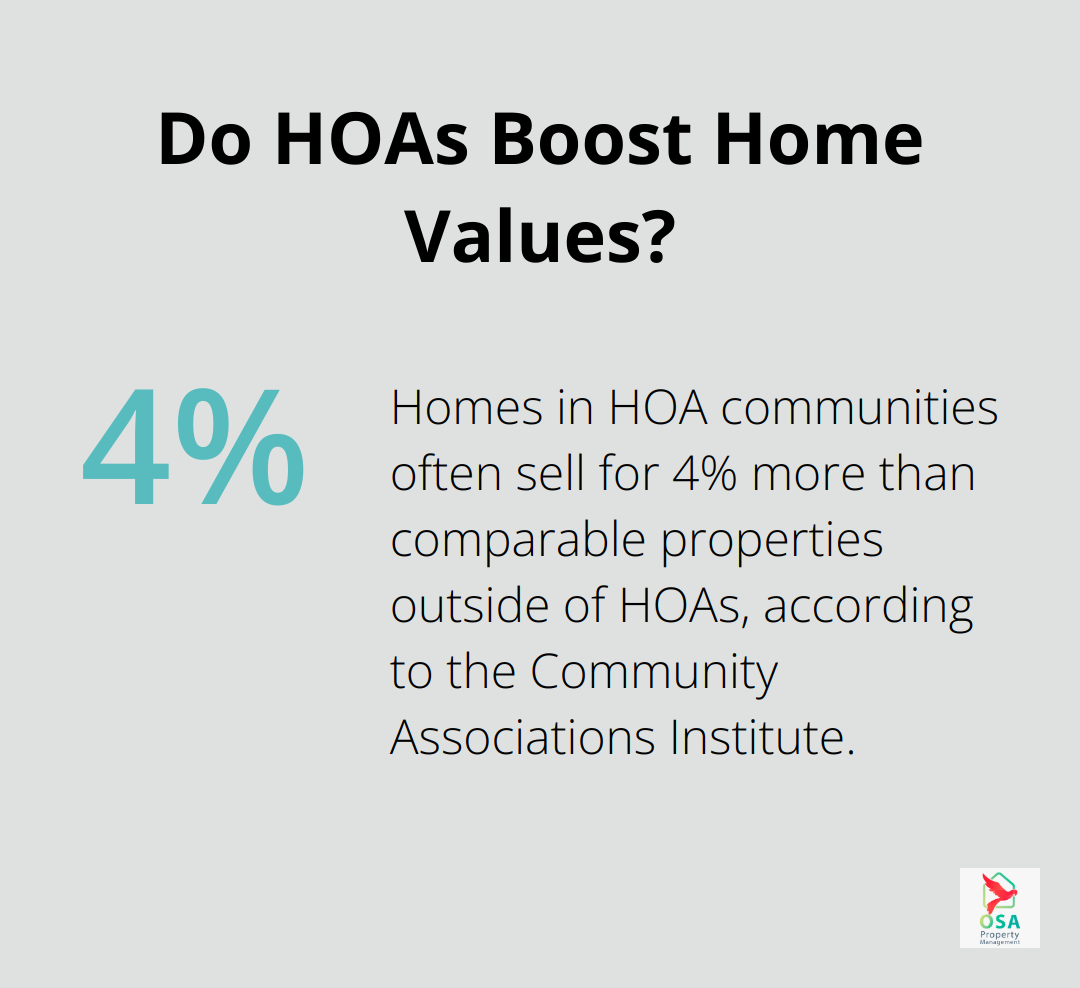
- Property Value: A well-run HOA can help maintain or increase property values over time. The Community Associations Institute reports that homes in HOA communities often sell for 4% more than comparable properties outside of HOAs.
- Cash Flow Management: Regular HOA fees require careful budgeting. It’s important to maintain a reserve for potential special assessments or fee increases.
- Legal Considerations: As the property owner, you’re responsible for HOA fee payments, even if your tenant fails to pay rent. Ensure your lease agreement clearly outlines responsibilities related to HOA rules and fees.
Understanding the nuances of HOA fees and their impact on your rental property allows you to make informed decisions that enhance your investment’s performance and appeal to quality tenants. In the next section, we’ll explore the tax implications of HOA fees for rental properties and how you can maximize your deductions.
Can You Deduct HOA Fees for Rental Properties?
Understanding HOA Fee Deductions
HOA fees for rental properties often qualify as tax-deductible expenses. This section will explain the guidelines set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and the conditions under which you can claim these deductions.
IRS Guidelines on HOA Fee Deductions
The IRS classifies HOA fees for rental properties as ordinary and necessary expenses. This classification allows property owners to deduct these fees from their rental income when filing taxes. However, this deduction applies only to properties used for rental purposes, not personal residences.
IRS Publication 527, which covers residential rental property, explicitly includes HOA fees in the category of deductible expenses. Landlords should familiarize themselves with this publication to understand their tax obligations and benefits fully.
Conditions for Deducting HOA Fees
While HOA fees are generally deductible, property owners must meet certain conditions:
- Rental Use: The property must serve as a rental. If you use the property for personal purposes part of the year, you can only deduct the portion of HOA fees that correspond to the rental period.
- Active Participation: You must actively participate in the rental of your property to claim these deductions. This participation includes making management decisions such as approving tenants, setting rental terms, and authorizing repairs.
- Timing of Deductions: HOA fees become deductible in the year you pay them, not when the HOA assesses them. This distinction is crucial for accurate record-keeping and tax reporting.
Strategies to Maximize HOA Fee Deductions
To optimize your HOA fee deductions, consider implementing these strategies:
- Detailed Record-Keeping: Maintain meticulous records of all HOA fee payments (including regular dues and any special assessments).
- Separate Personal and Rental Use: If you use the property personally for part of the year, calculate the exact percentage of time it serves as a rental. This calculation will help you accurately prorate your HOA fee deductions.
- Understand Special Assessments: While regular HOA fees are deductible, special assessments for improvements might require depreciation over time rather than immediate deduction.
- Consult a Tax Professional: Tax laws can be complex and change frequently. Working with a tax professional who specializes in rental property can ensure you maximize your deductions while staying compliant with IRS regulations.

The proper management of HOA fees and their deductions can significantly impact a rental property’s profitability. Understanding these rules and implementing smart strategies will help you optimize your tax benefits and improve your overall return on investment. In the next section, we will explore additional tax considerations for rental property owners and provide tips on how to streamline your tax preparation process.
How to Optimize Tax Benefits for Rental Properties
Implement a Robust Record-Keeping System
Accurate record-keeping forms the foundation of effective tax management. We recommend digital tools like QuickBooks or Stessa to track your HOA fee payments. These platforms allow you to categorize expenses easily and generate reports for tax season. Set up a system to immediately log each HOA payment, including the date, amount, and purpose (regular dues or special assessment). This practice will save you hours during tax filing.
Master Expense Allocation
For properties used for both personal and rental purposes, correct expense allocation is essential. Use a calendar to mark rental days versus personal use days. At year-end, calculate the percentage of time the property was rented. Apply this percentage to your annual HOA fees to determine the deductible amount. For example, if your property was rented for 300 days in a year (82% of the time) and your annual HOA fees were $3,000, you could deduct $2,460.
Leverage Professional Expertise
While independent tax handling is possible, working with a tax professional who specializes in rental properties can yield significant benefits. These experts stay current with tax law changes and can identify deductions you might overlook. They can help you navigate the complexities of deducting special assessments or advise on the tax implications of major HOA-funded improvements to your property.
Stay Informed on Tax Law Changes
Tax laws evolve frequently, and staying informed is key to maximizing your benefits. Subscribe to reputable real estate investment newsletters or join local landlord associations to receive updates on tax law changes. This proactive approach ensures you don’t miss out on new deductions or credits that could benefit your rental property investments.
Conduct Regular Tax Strategy Reviews
Tax optimization is an ongoing process. Schedule regular reviews of your tax strategies (ideally quarterly) to ensure you’re maximizing your benefits as tax laws and your property portfolio evolve. During these reviews, assess your current deductions, explore potential new tax-saving opportunities, and adjust your strategies as needed to align with your investment goals.

Final Thoughts
HOA fees for rental properties are tax-deductible, which can significantly reduce your taxable income. Proper documentation of HOA fee payments prepares you for tax season and potential audits. This practice ensures IRS compliance and helps identify opportunities to optimize your tax strategy.

Managing rental property expenses is a critical aspect of successful property investment. You must stay informed about tax laws, implement robust record-keeping systems, and seek professional advice when needed. These actions will help you navigate the intricacies of rental property taxation effectively.
Osa Property Management can help you manage your investments, including tax considerations for HOA fees and other rental property expenses. Our team of experts ensures your property is well-managed, compliant with local regulations, and optimized for profitability. We provide comprehensive services and local expertise in Costa Rica to support your rental property success.

