At Osa Property Management, we know that understanding tax benefits for rental property owners can significantly impact your bottom line.
Owning rental properties offers numerous financial advantages, and maximizing tax benefits is a key strategy for success.
In this post, we’ll explore the essential tax deductions and strategies available to rental property owners, helping you optimize your investment returns.
What Expenses Can Rental Property Owners Deduct?
Rental property owners can reduce their tax liability through various deductible expenses. Understanding these deductions can significantly boost investment returns.
Mortgage Interest and Property Taxes
Mortgage interest can be deducted on the first $750,000 ($375,000 if married filing separately) of indebtedness for rental property owners. This includes interest on mortgages, home equity loans, and lines of credit used for rental property purposes.
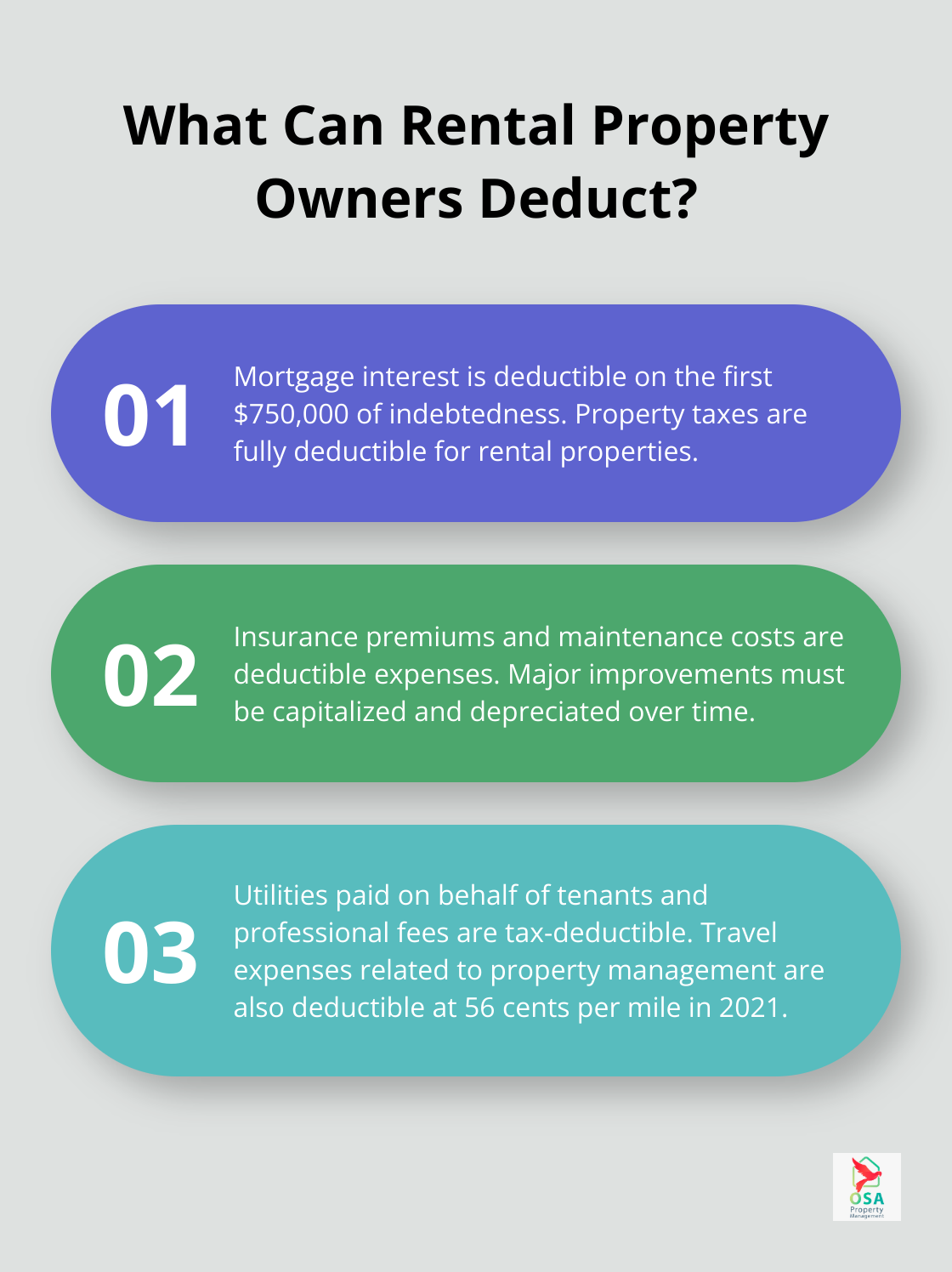
Property taxes also offer substantial deductions. Owners can deduct the full amount of property taxes paid on their rental properties. This benefit proves particularly advantageous in areas with high property tax rates. Detailed records of property tax payments help maximize this deduction.
Insurance and Maintenance Costs
Insurance premiums for rental properties are fully deductible. This encompasses landlord liability insurance, fire insurance, flood insurance, and any other policies specific to the rental property.
Maintenance and repair costs are deductible in the year they occur. The amounts paid to restore or improve property are capital expenditures or deductible ordinary and necessary repair and maintenance expenses. However, major improvements that add value to the property must be capitalized and depreciated over time. The IRS provides clear guidelines on what qualifies as a repair versus an improvement.
Utilities and Professional Fees
If landlords pay for any utilities on behalf of their tenants, these costs are deductible. This might include water, electricity, gas, or trash removal services.
Professional fees often go overlooked as a deduction. This category includes fees paid to property managers, attorneys, accountants, and other professionals involved in the rental business. For instance, fees paid to property management services (like Osa Property Management) are tax-deductible.
Travel and Home Office Expenses
Travel expenses related to your rental property are deductible. This includes mileage, airfare, and lodging costs incurred while visiting your property for management or maintenance purposes. The IRS allows a standard mileage rate (56 cents per mile in 2021) or actual expenses method for vehicle-related deductions.
Home office expenses may also qualify for deductions if you use a portion of your home exclusively for managing your rental properties. You can deduct a percentage of your home expenses (mortgage interest, property taxes, utilities) based on the square footage used for your rental business.
Maximizing these deductions requires meticulous record-keeping and a thorough understanding of tax laws. While this overview provides a starting point, consulting with a tax professional ensures you take advantage of all available deductions while staying compliant with tax regulations. Now, let’s explore another powerful tax tool available to rental property owners: depreciation.
How Depreciation Benefits Rental Property Owners
Understanding Rental Property Depreciation
Depreciation is a tax deduction that serves as a powerful tax tool that can reduce your taxable income from rental properties. This benefit allows you to deduct the market value loss and the costs of buying and improving a property over its useful life from your taxes. For residential rental properties, this period spans 27.5 years. You can deduct a portion of your property’s value each year, even if the property appreciates in market value.
Calculating Depreciation
To calculate depreciation, you must first determine your property’s cost basis. This includes the purchase price plus certain closing costs and improvements. Land value is not depreciable, so you must subtract that from your cost basis.

For example, if you purchased a rental property for $300,000, and the land is valued at $50,000, your depreciable basis would be $250,000. Divide this by 27.5 years, and you can deduct about $9,090 annually from your taxable rental income.
Long-term Implications and Recapture
While depreciation offers substantial tax benefits during ownership, you must understand the concept of depreciation recapture. When you sell the property, you may need to pay taxes on the accumulated depreciation at a rate of 25%. This often catches novice investors off guard and can lead to unexpected tax bills upon sale.
However, strategies like 1031 exchanges can help defer these taxes. Many successful investors use this strategy to build their real estate portfolios while deferring capital gains and depreciation recapture taxes.
Maximizing Depreciation Benefits
To maximize depreciation benefits, consider a cost segregation study. This analysis can be a powerful way to maximize depreciation deductions and minimize the tax burden for commercial property. While this can be complex, the tax savings often justify the cost of the study.
Depreciation stands as a valuable tool in your rental property tax strategy. When combined with other deductions and careful planning, it can significantly enhance your investment returns. As we move forward, we’ll explore additional strategies to maximize your tax benefits and optimize your rental property investments.
How to Optimize Your Rental Property Tax Strategy
Maintain Impeccable Records
Accurate record-keeping forms the foundation of a solid tax strategy. Use digital tools to track every expense related to your rental property. This includes receipts for repairs, utility bills, insurance premiums, and mileage for property-related travel. Property owners who maintain detailed records often find additional deductions they might have otherwise missed.
Leverage Pass-Through Deductions
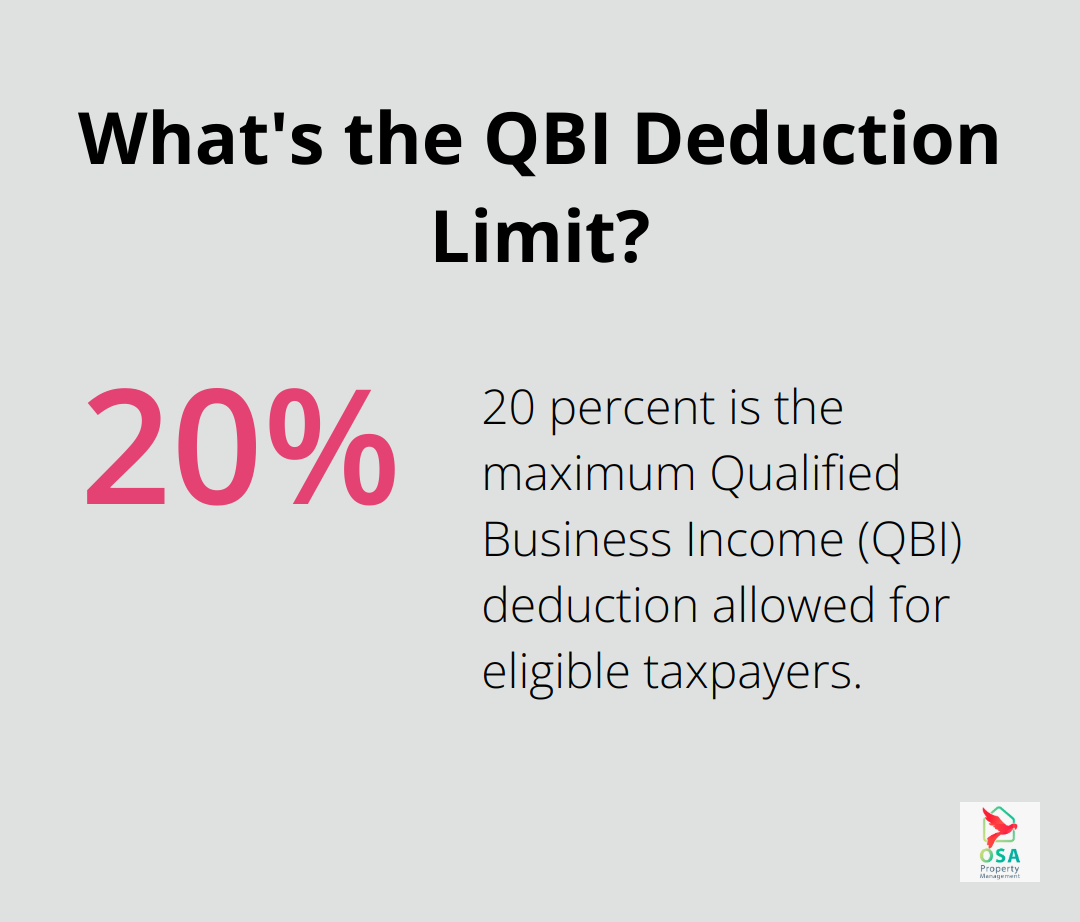
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act introduced a valuable benefit for rental property owners: the Qualified Business Income (QBI) deduction. This allows eligible taxpayers to deduct up to 20 percent of their QBI, plus 20 percent of qualified real estate investment trust (REIT) dividends. To qualify, your rental activities must meet specific IRS criteria to be considered a trade or business. Consult with a tax professional to ensure you meet these requirements and can take full advantage of this deduction.
Utilize 1031 Exchanges
A 1031 exchange is a powerful tool for deferring capital gains taxes when selling a rental property. This strategy allows you to continuously reinvest in like-kind properties, deferring capital gains taxes. While the rules are complex, the potential tax savings make it worth exploring. Many investors use this strategy to build their real estate portfolios while deferring significant amounts in capital gains taxes.
Employ Family Members Strategically
Hiring family members can be a tax-efficient way to manage your rental property business. You can deduct reasonable wages paid to family members as a business expense. This strategy can be particularly beneficial if you have children in lower tax brackets. For example, you could hire your child to manage social media for your rental properties, providing them with income while reducing your taxable business income.
Time Income and Expenses
Strategic timing of income and expenses can significantly impact your tax liability. Try to defer rental income to the following year if it will push you into a higher tax bracket. Conversely, if you anticipate being in a higher bracket next year, accelerate income into the current year. Similarly, timing major repairs or improvements can help balance your taxable income across tax years.
Implementing these strategies requires careful planning and often the guidance of a tax professional. While property management companies (like Osa Property Management) focus on providing top-notch services, they always recommend clients work closely with tax experts to optimize their rental property investments. The combination of professional property management with savvy tax planning can maximize the returns on your rental property investments and build long-term wealth.
Final Thoughts
Rental property ownership offers numerous tax benefits that can enhance investment returns. These advantages include deductible expenses, depreciation, and strategies like 1031 exchanges, which can significantly reduce tax liability. However, the complex nature of tax benefits for rental property owners necessitates expert guidance to maximize deductions and ensure compliance with IRS regulations.

The financial benefits of rental property ownership extend beyond immediate tax savings. As property values appreciate and equity builds, rental investments can become valuable assets for long-term wealth accumulation. Osa Property Management focuses on providing top-notch property management services in Costa Rica, while always recommending clients to work with tax professionals for optimized investments.
Unlocking the full potential of tax benefits requires staying informed and maintaining accurate records. The combination of expert property management and savvy tax planning can maximize returns on rental properties. This approach paves the way for long-term financial success and helps achieve investment goals through real estate.

